Innovative Contribution to Real-Time Ionospheric Scintillation Monitoring Using GNSS Observations
Mar 04, 2025
Candidate Yu Yin defended his thesis co-directed by Guillermo González and Angela Aragon-Angel on March 3 at Campus Nord. Titled "Innovative Contributions to Ionospheric Scintillation Monitoring using GNSS Observations," this thesis presents solid research that significantly advances scintillation monitoring with accurate, economical, and wide-coverage solutions, improving GNSS performance in complex ionospheric conditions
Ionospheric scintillation adversely impacts Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers by inducing signal amplitude fading and rapid carrier phase variations, degrading positioning accuracy in regions with high ionospheric activity. Monitoring scintillation is essential for ensuring the reliability of GNSS applications, particularly in precise positioning.
Scintillation monitoring traditionally relies on two indices, both typically derived from specialized GNSS receivers known as ionospheric scintillation monitoring receivers (ISMRs). However, the high cost of ISMRs limits their global deployment. Recently, geodetic receivers operating at 1 Hz have been proposed as alternatives for monitoring scintillation, benefiting from existing global GNSS networks.
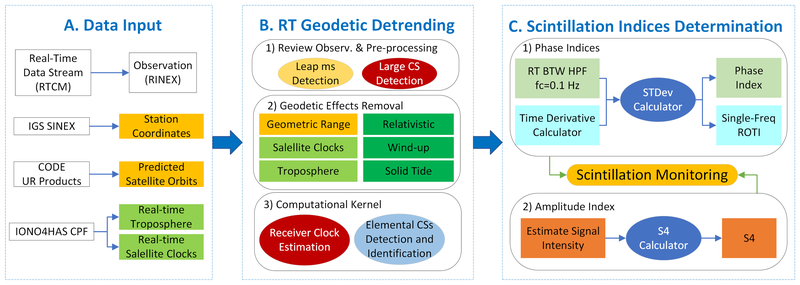
This research addresses key challenges in scintillation monitoring using Geodetic Detrending (GD) as the primary methodology. First, a novel index was introduced, it exhibits minimal dependence on receiver models or tracking strategies, making it a robust candidate for consistent global scintillation monitoring. Second, low-cost receivers were evaluated for their feasibility in scintillation monitoring, addressing challenges in deploying geodetic-grade receivers in uncovered or high-risk regions. Third, the GD technique was extended for real-time (RT) processing using RT satellite corrections and observations. A prototype RT GD framework was developed to deliver the scintillation indices in a global scale.
In conclusion, this research advances scintillation monitoring by offering a solution that is accurate, cost-effective, and capable of extensive coverage. These contributions have the potential to enhance GNSS performance under challenging ionospheric conditions.
Share: