Arjuna Castrillon has defended her doctoral dissertation on the physics of planetary nebulae
Jun 02, 2021
Arjuna Castrillon defended her thesis, co-directed by DFIS professors Jordi José and Domingo García-Senz on May 12, 2021 by teleconference. The thesis, entitled "Study of the physical properties of collided regions in planetary nebulae", presents an analysis of the morphology of microstructures present in planetary nebulae, as well as simulations of the motions of a star in the protoplanetary nebula phase.
This work addresses several topics in the study of the episodic jets (or bullets) ejected by the central source of a planetary nebula (PN). The presence of collimated bipolar outflows and point-symmetric morphologies are commonly observed in PNe, but the underlying physical mechanism is not fully understood. To address this problem, we have focused on the determination of the observational properties of Fast Low Ionization Emission Regions [FLIERs] and Low Ionization Structures [LIS] in PNe.
We have analyzed the morphology of a sample of selected PNe by means of anisotropic wavelet analysis applied to Hubble Space Telescope images. From this analysis, the spatial distribution of FLIERs/LIS and their characteristic sizes are determined.
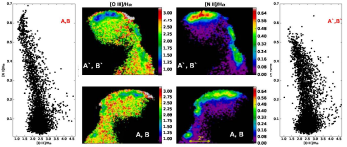
We have obtained spectroscopic data with a 2-dimensional coverage of several PNe of our sample. With these data, we mapped the physical conditions, excitation, and ionization structure of the observed bow shock-like structures (FLIERs) which provide the effect of the photoionizing heating from the central star on shocked regions associated with bipolar jets (i.e, “irradiated shocks").
Share: